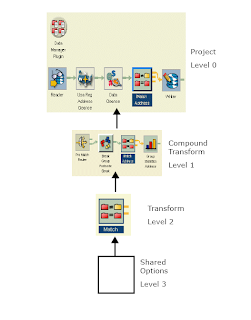
Project:Data Flow project.3 types of Projects(主要区别其实就是Reader & Writer的不同)
- Batch: A project run using batch processing. Batch processing executes a series of non interactive projects all at one time. Batch processing is particularly useful for operations that require the computer or a peripheral device for an extended period of time. Once batch processing begins, it continues until it is done or until an error occurs.The new project is based on the newproject_batch.xml file, and opens with a Data Manager plugin.
- Transactional : A project run using transactional processing. Transactional processing usually processes one record at a time. Transactional processing is accomplished with the Data Quality web service. The new project is based on the newproject_transaction.xml file, and opens with transactional Reader and Writer transforms and a Data Manager plugin.
- Integrated Batch: A project run using batch processing with an Integrated Batch Reader and an Integrated Batch Writer transform. This type of project can be used to pass data to and from an integrated application, including BusinessObjects XI Data Integrator Release 2. The new project is based on the newproject_integratedbatch.xml file, and opens with integrated batch Reader and Writer transforms and a Data Manager plugin. (可以为DI整合)
Transform: A transform consists of a group of options that perform a specific function (address cleansing, address validation, data cleansing, matching, and so on).A transform accepts data input from either a data source or another transform via a pipe, and will also output data to another transform or to a data target.
Compound Transform: A compound transform is a combination of transforms that show up as a single entity on the canvas.
Plugin: A plugin is a special kind of transform. A plugin must always be associated with
a transform of a specific type, or to an entire project.
Shared options: Transforms are made up of various files and subcomponents. With shared options, you can define a set of options for a given transform type, and then reuse those options among all transforms of that type.
Substitution variables: allow you to define a variable and a value for that variable.
Dataflow objects: are all of the things you just read about, includes projects, transforms, compound transforms, shared options, and so on.
Basic hierarchy of Data Object

Level of Data Objects
You will find more details from reference object panel in DQ.
 Note:
Note: The override & reuse concept between different levels needs more attention and further reading..
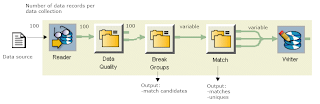
Data record: A data record is a row of data.The data record is constructed at runtime.
Data collection:A data collection is a group of data records. Early in the dataflow process, a fixed number of data records are grouped into data collections. Later, in preparation for
the matching process, a variable number of data records are grouped into
data collections of candidate matches. Finally, in the matching process, data records are split into data collections of matching records and uniques.
Data collections in the Reader transform : read at the same time and pass to next transform.
Data collections in the Match transform :The Match transform then receives the new data collections of potential matches one at a time and compares them, and then splits the data collections again into groups of matching and unique data records.
Data collections after the Match transform: All of the transforms downstream from the Match transform operate on the new match or unique data collections one at a time.
Low_Watermark and High_Watermark : Performance usage and to sync speed between each other.
Transactional project rules and tips:
- One collection in, one collection out :Every record in the collection passes (or fails) the conditions set up in the Filter transform, and the collection is sent to only one output pipe.
- Transactional Writer:You can only have one transactional Writer in a
transactional dataflow. - Aggregator transform: You cannot use an Aggregator transform in a transactional project. This transform’s task is to create collections based on criteria you select. In a batch project, there is a finite number of records and the Aggregator knows when the records stop coming. In a transactional environment, the project is left “open,” and therefore the transform would always be waiting for more records.
- Sorter transform: You can use a Sorter transform if you make sure that the Sort_Mode option is set to Collection_Sort.
- Flat files. If you are writing to a flat file, this file remains open until the transactional project is closed. Therefore, you may not be able to use this file if the project is still open.
- Batch Writers. You may find it useful to include a batch Writer in your transactional project to write to your database. You can route data from the transactional Writer to the batch Writer to save time in the future by allowing you to write to your database immediately after a transaction has occurred.
Field Name rule(output/input):
field_type.transform_type.class.parent_component.field_name
Filed overlapping is important!


